Diodes are simple device with 2 terminals – It allow current to only flow in 1 direction.
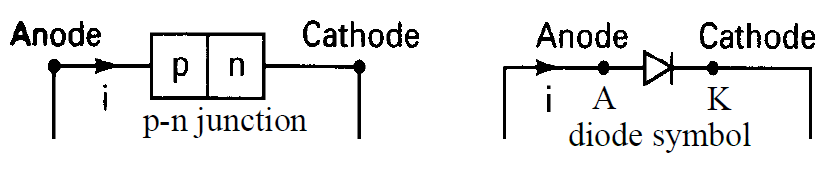
Electron flows from ANODE –> CATHODE direction
The diode characteristics can be placed in 3 regions
- Forward biased region VAK > V Forward ON (0.7-3 Volts)
- Reverse biased region VAK < 0 OFF or Blocking
- Breakdown region VAK <- VZK DAMAGED
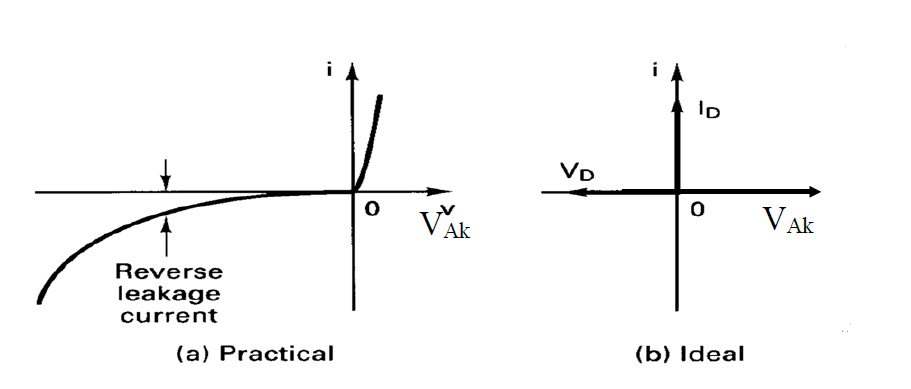
Normally there is some Reverse leakage current in practical which we will look into later.
Voltage Rating
Forward voltage Vd
For computing conduction losss and heat sink requirements.
Heat Loss calculation – P (W) = V (voltage) * I (Current)
For semiconductor silicon based – max temperature should not exceed 150C
(semiconductor when faced with extreme heat will short-circuit or go haywire)
Repetitive reverse maximum voltage VRRM
Gives the maxmium continuous blocking voltage. Anything more than this voltage, the diode will give way / blown.
Current Rating
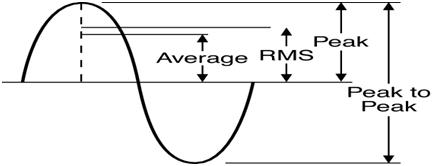
The maximum average forward current If(AV)
The maximum r.m.s forward current If(RMS)
RMS is roots mean square – the RMS is not an “Average” voltage, and its mathematical relationship to peak voltage varies depending on the type of waveform. The RMS value is the square root of the mean (average) value of the squared function of the instantaneous values.
The peak, forward current If(p)
The short burst of current the diode can take without damage


